The success of any educational organization depends heavily on the effectiveness of its teachers, who are tasked with transferring knowledge, supervising students, and enhancing the standard of instruction. Teachers’ job satisfaction has a significant impact on the lessons they teach since they are directly involved in transferring knowledge to students. In order to determine the effect of teachers’ job satisfaction (TJS) on students’ accomplishments, the researchers sought to analyze the empirical studies conducted over the previous 12 years (SA). To determine the characteristics that link to instructors’ job satisfaction and their effect on students’ achievement, thirty-two empirical studies were examined. The analysis of world-wide empirical research findings shows four types of results: (i) In some countries, teachers’ job satisfaction is low, but students’ achievement is high (Shanghai, China, South Korea, Japan, Singapore) (ii) In some countries, teacher job satisfaction is high, but student achievement is low (Mexico, Malaysia, Chile, Italy). (iii) In some countries, teachers’ job satisfaction is high, and so is student achievement (Finland, Alberta, Canada, Australia). (iv) In some countries, teacher job satisfaction is low, which has a negative impact on student achievement (Bulgaria, Brazil, Russia). In sum, irrespective of countries, highly satisfied teachers give their best to their students’ success, not only by imparting knowledge but also by giving extra attention to ensure the better achievement of each student. The review of this study makes it even more worthwhile to reflect on the need to avoid stereotypical considerations and assessments of any objective presentation of the phenomenon and to reflect more deeply on the need to assess the validity of the relationship study.

Teachers are the main part of the school education system. The factors affecting students’ achievement (SA) should be multifaceted. Among them, teachers are one of the important factors that affect students’ academic performance (Ma, 2012). Teacher job satisfaction (TJS) refers to teachers’ satisfaction with their current work, which can be divided into internal satisfaction and external satisfaction (Wang, 2019). TJS inquiry and analysis can help managers not only comprehend teachers’ professional attitudes and avoid burnout but also provide some guidance for management decision-making. Improving TJS will assist instructors in maintaining a high level of passion and enthusiasm for their profession for a long time, allowing them to play even better in the lesson and ensuring consistent teaching quality (Zong, 2016). Teachers must have proper work satisfaction in order to be fully ready to transmit knowledge and skills important for learners to develop in SA. Teachers have been revered as “nation builders”. More specifically, teachers who teach in colleges and train students into elites and have talents in different disciplines are the key to a nation. Low TJS may lead to lower levels of education (Borah, 2016).
Many studies show that TJS has a significant positive correlation with job performance. As an example, Hayati & Caniago (2012) found that higher job satisfaction is conductive to higher job performance, while Ejimofor’s (2015) finding shows triadic relationships in which it indicates that TJS improves teaching quality, and teaching quality has the direct effect of improving students’ quality. One of the most important topics in every academic organization is TJS and SA. TJS not only increases productivity but also helps promote a productive teaching and learning environment. Based on this, both school administrators and the government should give more attention to meeting the needs of teachers to improve their motivational level to achieve educational goals so as to improve student academic performance (Ihueze et al., 2018). Surprisingly, though some researchers did not find a substantial link between TJS and SA (Ejimofor, 2015; Borah, 2016), the intuition and popular expectation is that TJS affects SA significantly and directly (Fisher, 2003). Moreover, Lopes & Oliveira (2020), utilizing information from the 2013 Teaching and Learning International Survey, demonstrated that teacher job satisfaction is a vital element of teachers’ and schools’ performance as well as students’ academic and educational attainment (TALIS). They also discovered that aspects of interpersonal relationships are the most effective predictors of job happiness. They advised schools to improve by addressing interpersonal problems, especially in the classroom, where the majority of perceived job satisfaction tends to reside. The findings demonstrated that, (1) among the personal traits of teachers, teacher efficacy had significant effects on job satisfaction (You et al., 2017). As the factors affecting teachers’ job satisfaction vary depending on the context of different countries, this review included studies from different regions to give a comprehensive scenario of findings based on different regional factors. The review results have revealed the associated factors of teachers’ job satisfaction and their impacts on student achievement. The findings can be the subject of further exploration. The review study set out to accomplish the following objectives:
Between 2010 and 2021, the number of studies examining the impact of TJS on SA increased significantly.
Job satisfaction is one of the important topics in the fields of occupational psychology, organizational behavior, and human resource management to explore employee productivity and organizational effectiveness (Fisher, 2003). With the development of humanistic thinking and the concept of lifelong education, this concept has been generally accepted by people, and the academic community has increasingly paid attention to the work-related emotional experiences of different professional or occupational groups such as teachers, nurses, etc.
Generally speaking, TJS refers to a teacher’s overall emotional experience and cognitive expression of their occupation, working conditions, and state. The international community generally believes that, as a variable of emotional attitude, TJS itself not only covers different dimensions but, more importantly, TJS has an important and direct impact on teachers’ enthusiasm and commitment to teaching. Daily work efficiency and effectiveness are also powerful predictors of SA. In addition, from the perspective of organizational commitment, improving TJS is an important way to enhance teachers’ sense of identity and belonging to the school, as well as to improve teachers’ professional attractiveness.
From the perspective of logical inference, according to the important phenomenon of the mentoring effect in the rise of talent chains and talent groups in the history of scientific development, as well as the practical experience that “the greatest happiness of teachers comes from the extraordinary achievements of students,” and even the word “teacher” often used when praising teachers, judging from the phrases such as “famous teachers produce master apprentices” and “peaches and plums fill the world,” in practical work, SA should also be one of the important sources of TJS (Wang & Zhang, 2020).
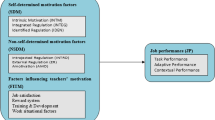
Different studies have used different elements that have direct, indirect, or even no impacts on the job satisfaction of teachers. In their research on college teachers’ job satisfaction, Shi et al. (2011) revealed that work treatment, job pressure, leadership behavior, gender, age, etc. have more or less influence on the job satisfaction of college teachers. Existing research usually divides the factors that affect TJS into four levels: individual, school, work, and others. The influencing factors at the individual level can be grouped into objective factors and subjective factors. Among them, objective factors include teachers’ educational background, teaching years (experience), gender, professional title, monthly income and workload, teaching subjects, etc.; subjective factors include occupational preference and work engagement.
The two main influencing variables at the school level are students and management. While the management aspect comprises the institutional culture of the school and student management, the student aspect includes the student’s learning environment. The professional growth environment, work pressure, learning exchange possibilities, etc. are examples of workplace factors. The location of the school (eastern, central, or western) and whether it is located in an urban or rural area are examples of other levels (Beijing Normal University Teachers’ Labor Market Research Group et al., 2021).
These elements can be categorized into three groups when considered collectively: the elements of the college professors themselves, the elements of the institutions, and the level of compatibility between individuals and roles. The author’s research focuses on the connection between these three variables and college professors’ job satisfaction (Shi et al., 2011).
Professional title, educational background, and job satisfaction are among the factors that teachers can control for themselves, but these variables have very weak correlations and cannot be used as explanatory variables in the regression equation. Age, on the other hand, has a weak correlation with job satisfaction but can be used as a variable to explain job satisfaction. Salary level is the school component that has the greatest impact on TJS. The primary output that teachers receive from the organization is compensation, which is also a key component that teachers demand from the organization. The degree of alignment between instructors’ expectations and their compensation is the most significant element determining TJS in terms of the matching of people to roles.
Defining a student’s grades is not an easy task. The most common metric of achievement is undoubtedly student performance on achievement exams in academic disciplines like reading, language arts, math, science, and history. The quality of schools and teachers, students’ backgrounds and situations, and a host of other variables all have an impact on academic attainment (Cunningham, 2012). The researchers looked at academic levels, achievement gaps, graduation and dropout rates, student and school development over time, and student success after high school.
Academic achievement is the ability to complete educational tasks. Such achievements can be general or topic-specific. Academic achievement refers to students’ scores in courses, curriculums, courses, and books that they have studied, expressed in the form of marks, percentages, or any other scale of marks (Borah, 2016). It is important to highlight that academic performance encompasses not only students’ achievement in tests and exams, but also their participation in social events, cultural events, entertainment, athletics, and other activities in academic institutions and organizations.
How to improve the academic performance of students is a popular topic in the field of education. After all, the purpose of education is to train students to become talents in society. Between 2010 and 2021, scholars from many different countries studied the relationship between TJS and SA. Many scholars’ studies have shown that there is a significant positive correlation between TJS and SA (McWherter, 2012; Crawford, 2017; Andrew, 2017; Iqbal et al., 2016). In these studies, the effects of TJS on SA were investigated, suggesting that it is fairly common in the literature to study the relationship between the two as a theme (Ejimofor, 2015; Borah, 2016).
Specifically, some districts have high SA but lower TJS than average schools. While some districts had high TJS, this did not improve SA. Therefore, it makes sense to understand the findings of these studies as a whole. What’s more, it is necessary to sort out the reasons for this divergence among numerous studies and make comparisons. The following questions serve as a guide for this study’s analysis of the findings in the literature on the effect of TJS on SA.
By examining previous research, this work seeks to characterize teacher motivation and assess the evaluation criteria and processes that account for student performance. The research method is systematically summarizing and analyzing based on a literature review, which helps us research and analyze the topic from a dialectical perspective. This study refers to the model of PSALSAR. The process of selecting documents starts with analyzing the topic, searching and classifying relevant documents, screening relevant documents from different sources according to the selection criteria, and finally extracting the most relevant documents for sorting out. Analysis (Bearman et al., 2012). The scope of this review also followed four criteria as outlined in the review work of Wayne & Youngs (2003).
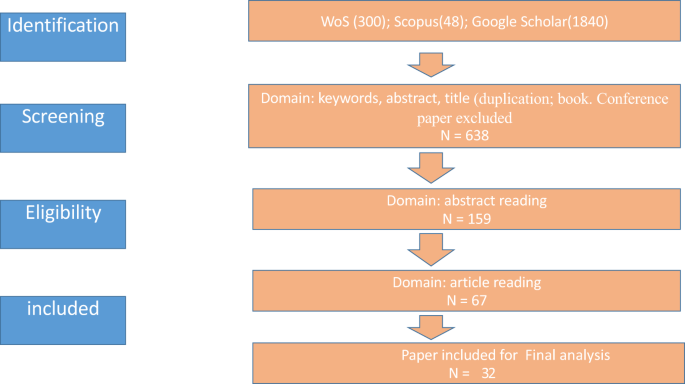
The data for this literature review was extracted from three major data sources: Web of Science, Scopus, Google Scholar, and HowNet. The review intended to take into account all recognized and relevant sources reporting on studies that are in English and falls within the duration of the study, which is a 12-year period from 2010 to 2021. The aim of the search is to locate all appropriate literature without expanding the search too much and retrieving a huge number of unrelated results. After applying an analytical inclusion/exclusion criterion to the 721 papers that were found, 32 papers were found to be applicable to the study’s objectives.
The databases were searched using the following terms: “career management of teachers,” “teacher job satisfaction,” “student achievement,” and “teacher job satisfaction and student achievement.”
There is much literature on the relationship between TJS and SA, many of which use TJS as a mediator, or TJS is just one of the variables to promote SA. Since the focus of this review was on the impact of TJS on SA, the literature search consisted of two phases to ensure that all relevant literature on the relationship between the two was included. In the first phase, which focused on TJS, the following search terms were used: “teacher job satisfaction”, “teacher work satisfaction” and “teacher satisfaction”, combined with the search term “SA”. In the second stage, the focus is on the effect of TJS on the SA selected from the first stage choices. After screening for keywords and selecting the year interval as 2010–2021, 26 documents were finally extracted for research. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) is an evidence-based framework that clearly defines the bare minimum of items to be included in systematic reviews and meta-analyses (Moher et al., 2009).
In order to check on the quality and validity of the data obtained, the most recent journals available on the topic were chosen. Also, a high priority was given to reading the findings and extracts of every journal before it was selected for review. Literature analysis adopts the selected research selected by narrative methods so that the author can understand the literature and find the mode by carefully reading and interpreting the research results (De Rijdt et al., 2013).
Next, each article is completely reread to determine the important part. Based on the content analysis method, the paragraphs of important information containing the answer to the hypothesis research question are encoded. In this literature review, as mentioned in an earlier section, the PRISMA is applied to the inclusion and exclusion criteria for the review. The table below depicts the details (Table 1).
In the past 12 years, most studies from different countries have paid much attention to the effect of teachers’ job satisfaction on student achievement. Most research shows that TJS will have a positive impact on students achievement (McWherter, 2012; Crawford, 2017; Andrew, 2017; Iqbal et al., 2016). Although there is still a small subset of studies showing no significant relationship between TJS and SA, the number of these studies is far lower than the number of studies that believe that TJS has a positive effect on SA (Ejimofor, 2015; Borah, 2016). There are many factors that affect TJS, but only work treatment, work pressure, co-worker relationships, etc. However, research shows that only classroom equipment and classroom size have a positive effect on both. Research shows that it is largely certain that national (or regional) culture has a non-negligible potential impact on teacher job satisfaction. Moreover, compared with the usual experience and stereotyped thinking that “students have good grades, so teachers’ job satisfaction should also be high”, the degree of influence of cultural differences on teachers’ job satisfaction, or at least the degree of correlation between the two, is more obvious and relevant. The review of this study makes it even more worthwhile to reflect on the need to avoid stereotypical considerations and assessments of any objective presentation of the phenomenon and to reflect more deeply on the need to assess the validity of the relationship study. As in the case of measuring teacher job satisfaction, the extent to which cultural differences affect teacher job satisfaction cannot be ignored. This is why it is important for scholars to develop a framework for measuring teachers’ job satisfaction according to cultural contexts and specific social needs and to give more dimensions to reflection and further measurement. Only on this basis can the overall level of teacher satisfaction be improved, thus increasing the overall level of teacher effectiveness and well-being, and better motivating students to engage in teaching and learning activities that lead to better quality learning outcomes.
Data sharing is not applicable to this research as no data were generated or analyzed